Private cloud is, as the name suggests, a completely exclusive hardware and software resource dedicated to a single user (or customer). You might also hear it referred to as a corporate or internal cloud.
With increasingly strict compliance regulations, many companies are turning to this sole-use model to ensure they meet these requirements. Others choose to do so because they deal with sensitive data, such as financial or medical information.
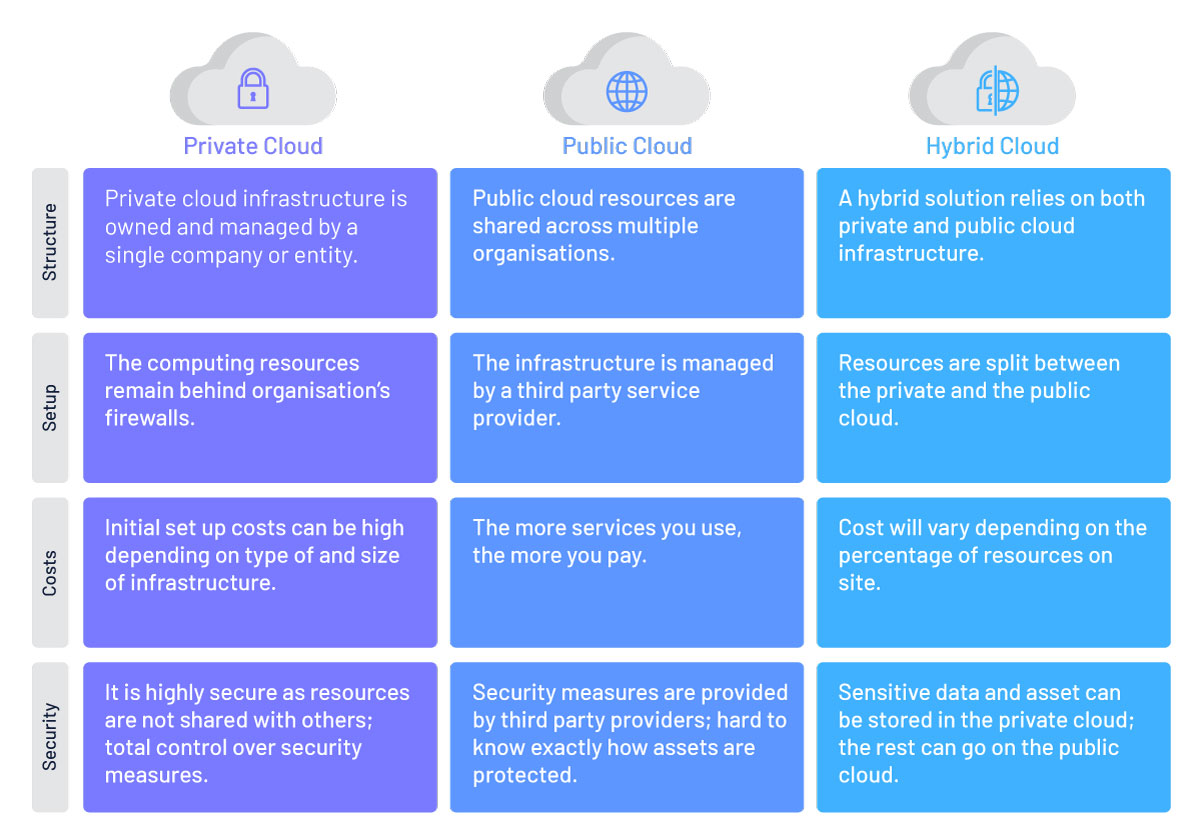
Private cloud vs. public cloud: the crucial differences
While the architecture of private cloud is of a similar make-up to public cloud technology, there are some important differences.
- A private cloud provides a single-tenant environment. The public cloud is shared by many users.
- Private clouds are most usually hosted on-premises in a purpose-built data centre or micro data centre (MDC). The public cloud is hosted in enormous central data centres located at strategic points around the world. However, some companies do operate a private cloud architecture using rented off-site infrastructure with exclusive access.
- Private clouds can be managed in-house or partially/fully outsourced to a service provider. Public cloud services are completely outside of the individual user’s management, with the service provider owning and maintaining the infrastructure.
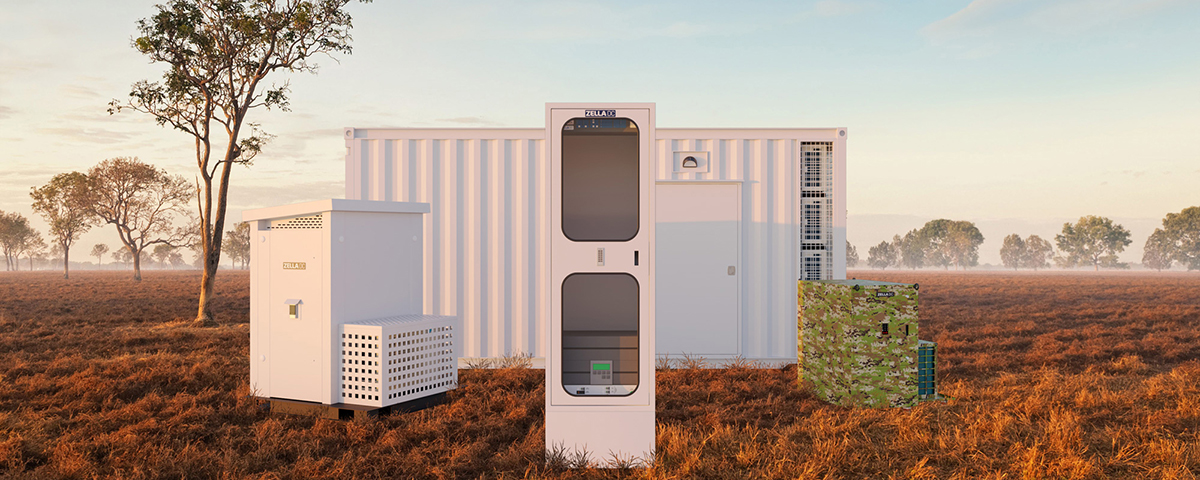
Private cloud setup
A private cloud setup is based on the same strategies as its public cousin. Computing resources benefit from various automation to speed up tasks and remove the need for human intervention. Virtualisation allows scalability and elasticity in the same way as the public cloud, ensuring the system can flex and scale in response to traffic and usage needs. Companies can also appoint administrators to run a centralised management control software to create a data environment that’s bespoke to business needs.
The adaptability this offers also extends to easily moving workloads from the private environment to public – or to utilise a hybrid cloud model that uses both to their advantage.
The advantages of private cloud
As already mentioned, the security offered by private cloud is perhaps the most important. But the benefits don’t stop there. Private cloud users also have:
- Customisation ability: Servers and storage can be set up optimally for company needs. Software can be customised, add-ons built in and any other changes made whenever needed
- Ease of regulatory standards compliance: When utilising public cloud services, businesses are forced to rely on what’s offered by the service provider. With private cloud, companies can determine exactly what’s needed – often ensuring better data security for their customers.
- Enhanced security regulation: Everything runs behind the company’s own firewall, allowing far greater influence over security and access control
Private cloud storage options

As private cloud architecture becomes more widespread, so have the choices for storage and management. The key areas to understand are:
- Private cloud storage
- Virtual private cloud
- Managed private cloud
Private cloud storage
This is most usually located on-site. Larger companies may have a dedicated server room, but many users are now leaning towards the cheaper and more flexible option of MDCs. These small, scalable and versatile units provide ultra-secure data storage that doesn’t require the massive outlay associated with traditional server rooms. In combination with private cloud architecture, using MDCs creates a wholly secure online environment that’s fully within company control.
Other advantages brought about by MDC storage options include:
- Data storage in any location – including remote locations and those without dedicated mains electricity connection (can run on either AC or DC power)
- Keeps data close to where its generated, so ideal for edge computing needs
- Storage can be increased whenever needed
- Mobile – can easily be moved to an alternative location
- Cost-effective storage – cheaper than traditional onsite server rooms
Virtual private cloud
A service from a public cloud provider that allows an isolated space within a public cloud infrastructure. The customer benefits from a private cloud-like environment, although this is not quite as exclusive as an in-house option. It is, however, cheaper to build and run, as well as having fewer management complexities.
Managed private cloud
This is a popular model offered by providers to fully manage the service, with data storage usually being in-house. There are some instances where they may also offer a wholly private space within their own data centre. This allows for more customisation than a virtual private cloud. It is, however, more expensive than a self-management option.
The benefits of private cloud are many – with security and customer confidence being at the very top of the list. Whether you choose a public, private or hybrid option, combining this with the advantages of micro data centre technology is a powerful way for companies to meet their many responsibilities in a cost-effective and flexible manner.
Find more about micro data centres or get in touch today to discuss how an MDC can super-charge the benefits of private cloud infrastructure.






