As Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to advance, it has the potential to revolutionise the way we use and interact with technology. One area where AI is having a significant impact is in edge computing. Edge computing refers to the practice of processing data at or near the source, rather than sending it to a centralised data centre or cloud for processing. In this blog, we will explore how AI is affecting edge computing and the implications of this for businesses and consumers.
AI and edge computing: a perfect match
Edge computing and AI are a perfect match for several reasons. Firstly, edge computing provides low-latency processing, which is essential for applications that require real-time decision-making. AI algorithms require large amounts of data to be processed quickly to provide accurate results. By processing data at the edge, businesses can reduce latency and improve the accuracy and speed of AI-driven applications.
Secondly, edge computing provides improved security and privacy. By processing data at the edge, businesses can ensure that sensitive data is kept within the organisation’s network, rather than being sent to a centralised cloud where it is more vulnerable to cyber attacks. This is particularly important for applications that handle sensitive information such as healthcare or financial data.
Finally, edge computing provides cost savings by reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to a centralised data centre or cloud for processing. This reduces the amount of bandwidth required and can result in significant cost savings for businesses.
Applications of AI in edge computing
AI is already being used in a variety of edge computing applications. One example is in the field of autonomous vehicles. AI algorithms are used to analyse data from sensors in real-time, allowing the vehicle to make decisions about speed, direction, and braking. By processing this data at the edge, the vehicle can make decisions in real-time without the need to send data to a centralised cloud for processing.
Another example is in the field of industrial IoT. AI algorithms can be used to analyse data from sensors in real-time, allowing businesses to monitor and optimise production processes. By processing data at the edge, businesses can improve the accuracy and speed of decision-making, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings.
The future of AI and edge computing
As AI continues to advance, we can expect to see even more applications of AI in edge computing. One area that is likely to see significant growth is in the field of healthcare. AI algorithms can be used to analyse data from wearable devices, providing real-time monitoring and analysis of patient data. This can lead to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Another area where we can expect to see growth is in the field of smart cities. AI algorithms can be used to analyse data from sensors placed throughout the city, providing real-time insights into traffic patterns, energy usage, and air quality. By processing this data at the edge, cities can improve the efficiency of public services and reduce costs.
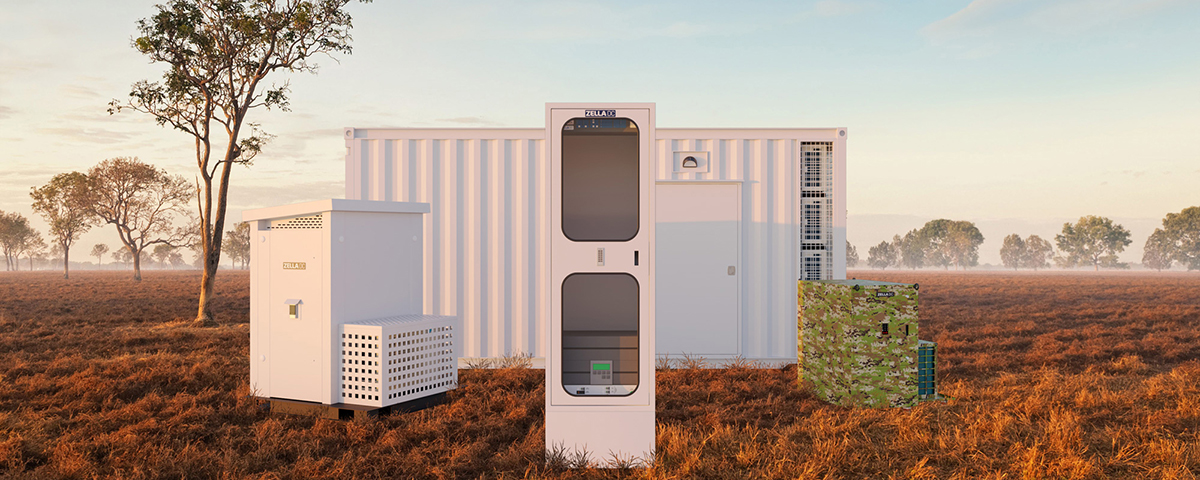
The role of micro data centres
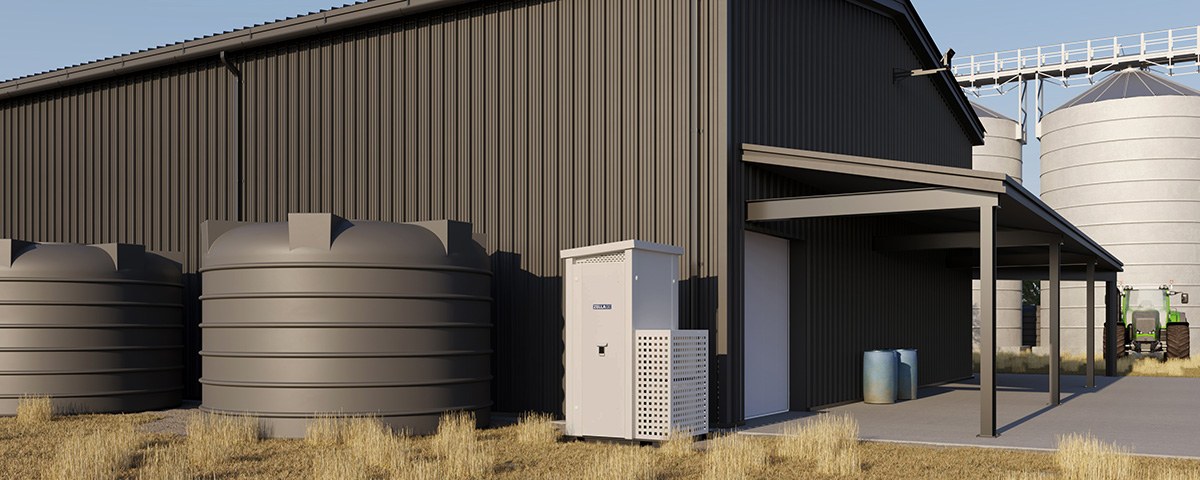
Micro data centres are a critical component of edge computing. They are small, self-contained data centres that are deployed close to the edge devices. Micro data centres are designed to provide local processing power, storage, and network connectivity, enabling businesses to process data at the edge quickly. They are becoming increasingly important as businesses look to take advantage of the benefits of edge computing.
The role of micro data centres in edge computing is to provide low-latency processing and real-time data analysis. They are ideal for applications that require fast, accurate decision-making, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial IoT. Micro data centres are also highly secure, with built-in security features to protect against cyber attacks.
Another advantage of micro data centres is their flexibility. They can be deployed quickly and easily, making them ideal for businesses with multiple locations or those that need to move their data centres frequently. They are also scalable, allowing businesses to add processing power and storage as needed.
One example of the use of micro data centres in edge computing is in the field of retail. Retailers are using micro data centres to process data from sensors in real-time, allowing them to analyse customer behaviour and adjust their marketing strategies accordingly. By processing data at the edge, retailers can provide a personalised shopping experience for their customers, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Conclusion
AI is having a significant impact on edge computing. By processing data at the edge, businesses can improve the speed and accuracy of decision-making while reducing costs and improving security. As AI continues to advance, we can expect to see even more applications of AI in edge computing, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings across a wide range of industries.
Our range of edge-ready micro data centres is perfect for AI applications in most industries and environments. Have a look at our range of indoor micro data centres, outdoor micro data centres, or containerised solutions – or get in touch to find out how we can help you solve your edge computing challenges.






