SOLUTIONS
What are micro data centres?
Understanding the basics of micro data centres
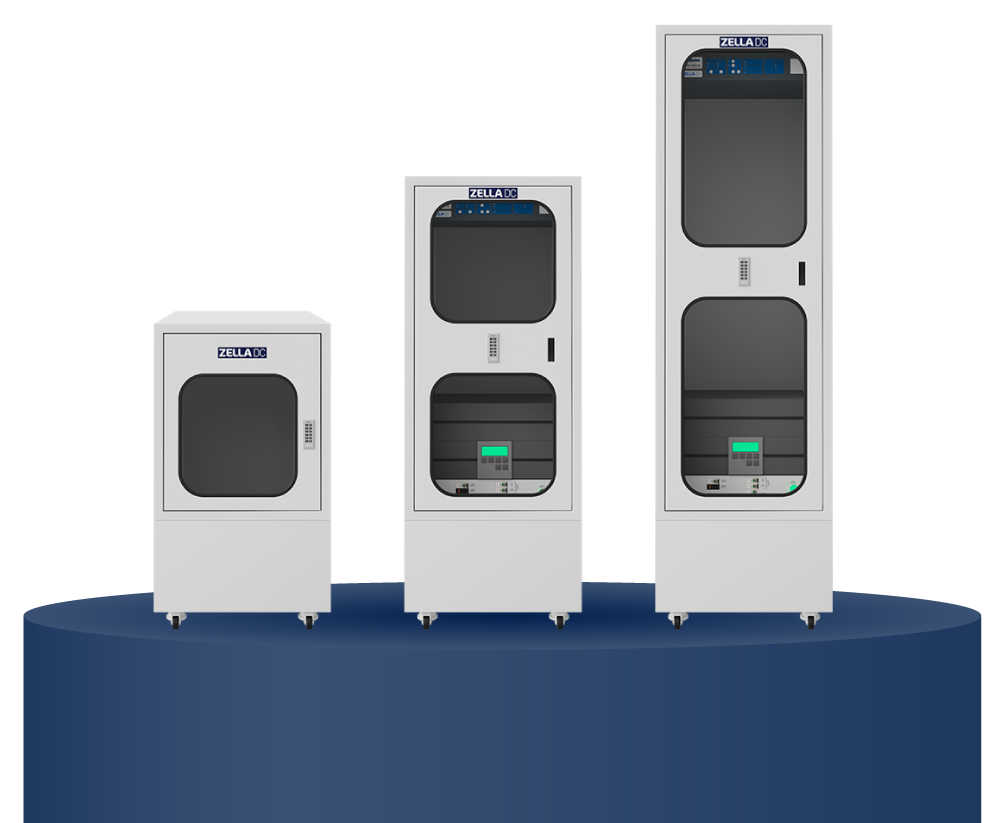
Micro data centres are compact, self-contained units designed to deliver the core functions of a traditional data centre but in a smaller, more manageable package. Micro data centres, also known as MDCs, are engineered to provide computing power, storage, and networking capabilities at or near the location where data is being generated, which is often referred to as “the edge” of the network.

Key features of micro data centres
Compact and modular design
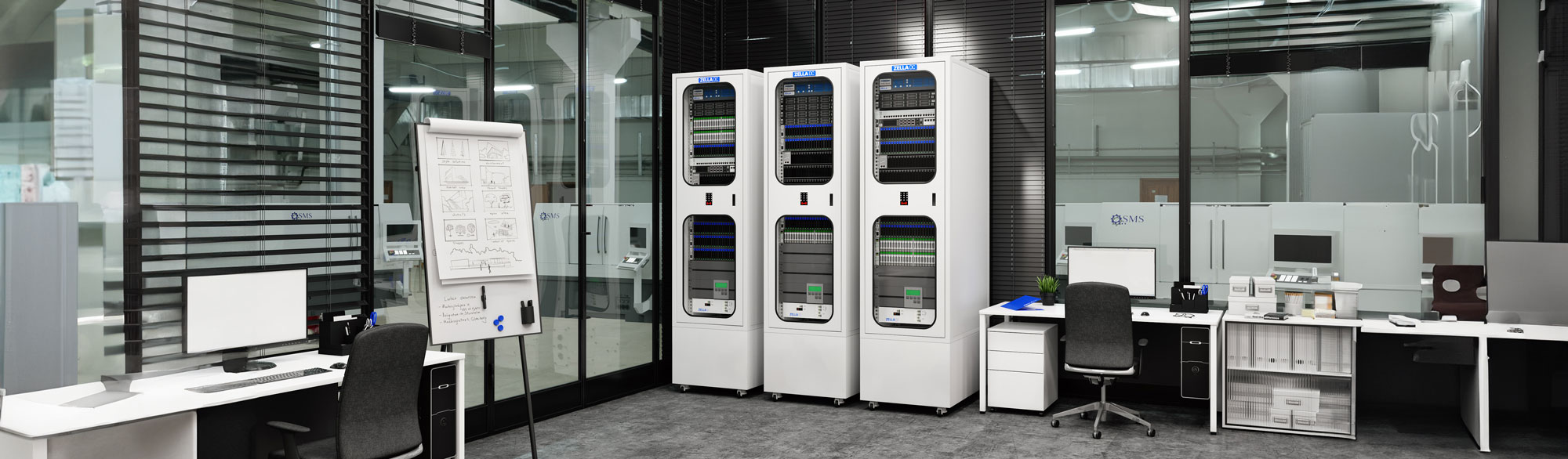
Micro data centres are designed to be small and modular, allowing for easy installation in various environments, including offices, remote sites, or industrial settings. Their compact size makes them ideal for locations where space is at a premium.
Self-contained
An MDC integrates all necessary components within a single enclosure, including power, cooling, security, and fire suppression systems. This self-contained design ensures reliability and ease of deployment.
Scalability
Micro data centres can be scaled according to the needs of the business. Additional units can be added to increase capacity as demand grows, offering a flexible and cost-effective solution.
Edge computing
By processing data closer to its source, micro data centres reduce latency and improve speed and performance. This is particularly beneficial for applications requiring real-time data processing, such as IoT (Internet of Things) devices, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities.

Enhanced security
Micro data centres offer robust security features, including biometric access control, encryption, and firewalls, to protect sensitive data. Physical security measures such as vandal-proof and waterproof construction further enhance their resilience.

Energy efficiency
These units are designed to be energy-efficient, utilising advanced cooling systems and power management technologies to minimise energy consumption and reduce operational costs.
Benefits of micro data centres

Reduced latency
By positioning the data closer to the end user, micro data centres significantly reduce the time it takes for data to travel back and forth, improving overall performance and user experience.
Cost-effective
Compared to traditional data centres, micro data centres are more affordable to deploy and maintain. They require less physical space, lower power consumption, and reduced cooling requirements.
Quick deployment
Micro data centres can be rapidly deployed to meet immediate business needs. Their modular design allows for quick installation and easy integration with existing IT infrastructure.
Reliability
With built-in redundancy and robust design, micro data centres ensure high availability and reliability, making them a dependable choice for critical applications.
Flexibility
The ability to deploy micro data centres in diverse environments, from urban settings to remote locations, provides businesses with the flexibility to support various applications and workloads.
Applications of micro data centres
Micro data centres are versatile and can be deployed across various industries to address specific needs and challenges. Their compact, self-contained design and ability to process data at the edge make them an ideal solution for environments where space, speed, and reliability are critical. Below are some key industries and scenarios where micro data centres are making a significant impact, enhancing efficiency, security, and performance.

Healthcare
Micro data centres support real-time data processing for medical imaging, electronic health records, and telemedicine applications, ensuring fast and secure access to patient information.

Telecommunications
Telecom companies use micro data centres to enhance network performance, deliver faster services, and support the growing demand for mobile data.

Education
Educational institutions leverage micro data centres to provide reliable access to online resources, support e-learning platforms, and manage large volumes of data generated by research activities.

Smart mining
In the mining industry, micro data centres facilitate real-time monitoring and control of mining operations, improving safety and operational efficiency.
Micro data centres Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a data centre and a micro data centre?
In contrast to traditional data centres, micro data centres arrive preassembled, pretested, and fully integrated, ready to house servers, storage, and networking equipment. This integration simplifies setup and reduces the complexity typically associated with deploying new IT infrastructure.
What is the difference between a server room and a micro data centre?
A server room is a designated space within a building that houses servers and related IT equipment. It typically requires separate infrastructure for cooling, power, and security. In contrast, a micro data centre is a self-contained unit that integrates all these components within a single enclosure.
Micro data centres are designed to be more flexible and easier to deploy, providing a complete, turnkey solution for IT infrastructure needs. They are also optimised for edge computing, offering enhanced performance and reduced latency by processing data closer to its source.
How do micro data centres support edge computing?
Micro data centres support edge computing by processing data close to its source, reducing latency and improving speed and performance. This is essential for applications that require real-time data processing, such as IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities.
Are micro data centres energy-efficient?
Yes, micro data centres are designed to be energy-efficient. They use advanced cooling systems and power management technologies to minimise energy consumption and reduce operational costs, making them a sustainable choice for businesses.
Zella Pro micro data centre
A Zella Pro is a compact, portable, and secure micro data centre that eliminates the need for a traditional on-premise server room.



